Travelling by flights is very popular nowadays and is predicted that in Europe the number of passengers in 2035 travelling by airplanes will be as twice as that in 2012, the number of flights in 2035 will increase 1.5 times the level of traffic in 2012. However, it can create many challenges in terms of sustainability and competitiveness with the current operations of aviation. For example, due to the limited capacity, in 2035 many flights cannot be accommodated or equivalently, a lot of passengers cannot travel by flight. Moreover, the problems about the environmental impact, security and safety are going to grow as well.
Therefore, the European Commission has adopted some significant changes in Air Traffic Management (ATM) system. One of the benefit change to ATM system is Trajectory Based Operations (TBO). The TBO concepts about sharing and managing trajectory information among airspace users (AUs) provide an opportunity for ATM system to improve management more efficient based on the users preferences and priorities. Here the methodology framework looks like:
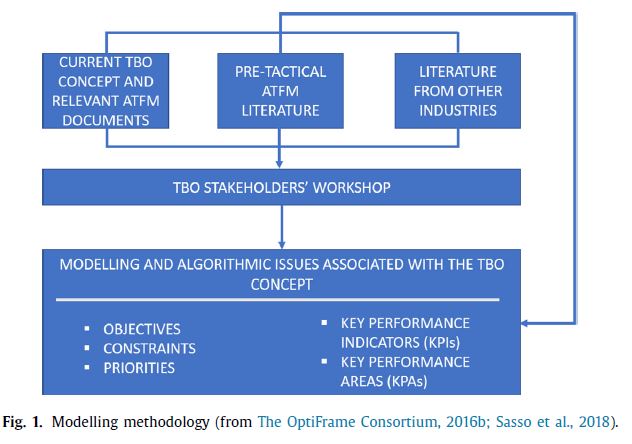
Dal Sasso et al. (2018) develop 4-D trajectory based multi-objective model with the constraints of the system and the stakeholders’s preferences and priorities, where input is the preferred 4D-trajectory of all aircrafts in the pre-tactical planning. Here the 4D trajectory of a flight consists of time periods and three spatial dimensions (lateral and vertical dimension). The objectives including:
- Minimization of the total delay time from the scheduled time of operations consisting of the airborne delay and ground holding delay.
- Minimization of the cost of rerouting from the preferred routes, i.e. cost of fuel.
- Minimization of total cost of travelling through the charging zones of flights.
The optimal solutions are non-dominated, since the 4-D trajectories solution can be managed before departure and during flight. Moreover, the solution will satisfy the requirement of TBO concept by incorporating the ATM stakeholders’s opinions.
AUs can express their own views about their preferences in term of deviation from their preferred trajectories, e.g. delay, rerouting or flight altitude. The preferences are taken into considerations in two ways. Firstly, the stakeholders will express their own idea about how their flights trajectories should be deviated from its preferred one. Next, the model will rank the deviation for each flight and then, assign the cost for the alternative trajectories. Secondly, the three objective functions are considered as ideal and then, the preferences of the AUs can be accounted for by determining how well each of them can achieve the AUs individual interests.
The prioritization framework provide AUs managing more flexible. The model in paper considers prioritization at the planning phase. AUs can rank their flights from highest and lowest in 1:10 scale. And they will decide how the total delay time should be allocated among their flights corresponding to its priority ranking. Here the total amount of delay of each AU are determined by the network manager running simulation after submission of their preferred flight trajectories request in order to ensure the fairness among the AUs.
There are some specific assumption for models:
- On one time period a flight can traverse one arc at most once.
- If a flight is planned to change the altitude during the next time period, it can begin to descend or ascend during the current time period for a smooth transition of flight levels.
- The possible flight paths of one flight in 2-dimension can be described by a directed graph. Without loss of generality, the graph is considered as acyclic graph, i.e. having no cycle in graph.
Constraints are defined to ensure that each aircraft is assigned a single route with prioritization constraints and that number of flights leaving, arriving to the airport and entering the en-route sectors can not be exceeded the corresponding maximum capacity defined by the air traffic controllers.

Table 1. Quadrant Shrinking method Algorithm.
Before implementing the model to solver, it is wise to keep the number of variable as low as possible, which is called by the pre-processing step. Then Dal Sasso et al. (2018) have implemented the quadrant shrinking method since it very simple, but outperformed compared with the other existing methods and moreover, the method only require solving two single-objective integer programs in order to compute all non-dominated solutions. With the computational experiments, the model can handle large-scale instances up to 10000 flights, however the computational time is still the impractical for practical use. To circumvent the difficulty, a faster and more efficient algorithm is required.
Reference:
1. Incorporating Stakeholders’ priorities and preferences in 4D trajectory optimization. / Dal Sasso, Veronica; Djeumou Fomeni, Franklin; Lulli, Guglielmo; Zografos, Konstantinos G.
In: Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, Vol. 117, No. A, 11.2018, p. 594-609.