DECORATION XXV. THE BASE 339
seen from above, and the eye is drawn to it as one of the most important features of the whole base; therefore it is a point of immediate necessity to substitute for its harsh right lines (c d, c e) some curve of noble abstract character.
§ 12. I mentioned, in speaking of the line of the salvia leaf at p. 270, that I had marked off the portion of it, x y, because I thought it likely to be generally useful to us afterwards; and I promised the reader that as he had built, so he should decorate his 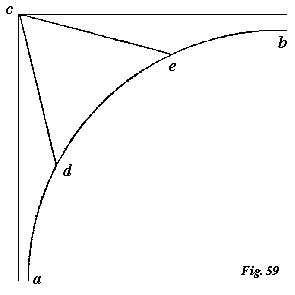 edifice at his own free will. If, therefore, he likes the above triangular spur, c d e, by all means let him keep it; but if he be on the whole dissatisfied with it, I may be permitted, perhaps, to advise him to set to work like a tapestry bee, to cut off the little bit of line of salvia leaf x y, and try how he can best substitute it for the awkward lines c d, c e. He may try it any way that he likes; but if he puts the salvia curvature inside the present lines, he will find the spur looks weak, and I think he will determine at last on placing it as I have done at c d, c e, Fig. 60. (If the reader will be at the pains to transfer the salvia leaf line with tracing paper, he will find it accurately used in this figure.) Then I merely add an outer circular line to represent the outer swell of the roll against which the spur is set, and I put another such spur to the opposite corner of the square, and we have the half base, Fig. 60, which is a general type of the best Gothic bases in existence, being very nearly that of the upper shafts of the Ducal Palace of Venice. In those shafts the quadrant a b, or the upper edge of the lower roll, is 2 feet 13/8 inches round, and the base of the spur, d e, is 10 inches; the line d e being therefore to a b as 10 to 253/8. In Fig. 60 it is as 10 to 24,
edifice at his own free will. If, therefore, he likes the above triangular spur, c d e, by all means let him keep it; but if he be on the whole dissatisfied with it, I may be permitted, perhaps, to advise him to set to work like a tapestry bee, to cut off the little bit of line of salvia leaf x y, and try how he can best substitute it for the awkward lines c d, c e. He may try it any way that he likes; but if he puts the salvia curvature inside the present lines, he will find the spur looks weak, and I think he will determine at last on placing it as I have done at c d, c e, Fig. 60. (If the reader will be at the pains to transfer the salvia leaf line with tracing paper, he will find it accurately used in this figure.) Then I merely add an outer circular line to represent the outer swell of the roll against which the spur is set, and I put another such spur to the opposite corner of the square, and we have the half base, Fig. 60, which is a general type of the best Gothic bases in existence, being very nearly that of the upper shafts of the Ducal Palace of Venice. In those shafts the quadrant a b, or the upper edge of the lower roll, is 2 feet 13/8 inches round, and the base of the spur, d e, is 10 inches; the line d e being therefore to a b as 10 to 253/8. In Fig. 60 it is as 10 to 24,
[Version 0.04: March 2008]
