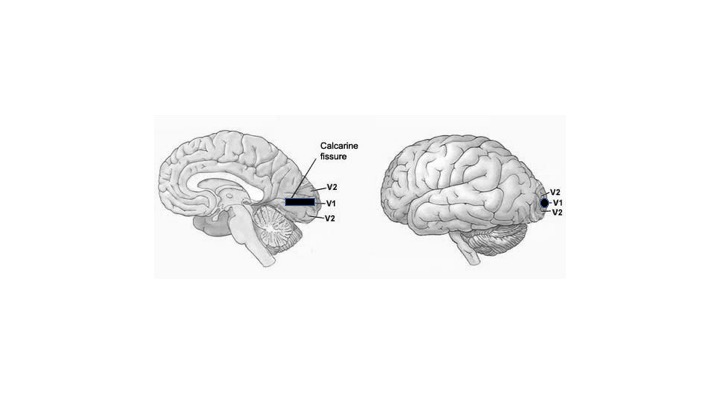
The part of cortex that receives direct visual input from the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, which in turn gets direct retinal input. Also called the striate cortex (due to bands or stripes of myelinated axons) and as area V1 in non-human primates and Brodmann area 17 in humans. It is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each area in the primary visual cortex receives input from the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus that in turn is a source of signals from the contralateral visual hemifield. While the primary visual cortex assumes a relatively small portion of the surface of the cortex in the occipital lobe, it ‘invades’ well into the calcarine nucleus (see figure below). In this way, it takes up a significant part of the overall surface of the cortex. Neurons in the visual cortex fire action potentials when visual stimuli appear within their receptive field. A long-standing finding is that neurons in the primary visual cortex are arranged in columns with well-defined functional properties. Thus, one column in the contralateral eye responds mainly to visual stimuli in a particular orientation (e.g., horizontal vs vertical) while neurons in another do so mainly to an upright orientation via the ipsilateral eye. The columns themselves are further organized into assemblies or modules. Areas in the occipital lobe (viz., the extrastriate cortex) are also involved with vision. These areas have been associated functionally in terms of the distinction between the dorsal and visual streams.