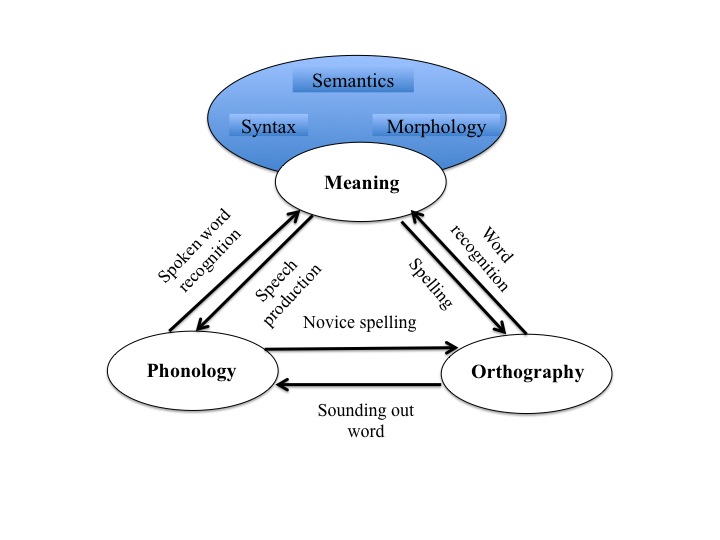
A set of skills that include the ability to read words directly without translating them to sound, usually with automaticity. In fact, they involve acquiring the ability to identify patterns of specific letters as words, eventually giving rise to word recognition. There is a unification among spelling, pronunciation and meaning of a word, such information being accessed simultaneously on visual presentation of a word. Such an achievement is challenging in English as its orthography is characterized by both polyphony (viz., a grapheme representing more than one phoneme) and polygraphy (viz., a phoneme representing more than one grapheme). But the development of reading requires not only orthographic reading skills, but also phonological reading skills and their integration to result in understanding the meaning of words. The figure depicts the basic components in this process.