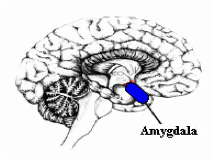
Also called the amygdaloid nucleus, it is a key, almond-shaped, bilateral structure in the limbic system of the forebrain (see figure below), involved in emotion recognition and other social emotional functions such as fear, aggression and defensive behaviours, as well as learning and memory. Connected with the prefrontal cortex, hypothalamus, hippocampus and cingulate gyrus. Many common tranquillising and sedative drugs act on the amygdala.