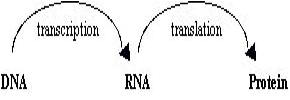
A term coined by Francis H.C. Crick (1916-2004) in 1958, it states the idea that genetic ‘information’ flows in only one direction from DNA -> RNA -> protein. Put another way, it holds that DNA makes (or transcribes) RNA makes (or translates) proteins that in turn facilitate the previous two steps as well as the replication of DNA (see figure below). Accordingly, the flow can now be given as DNA -> DNA -> RNA -> protein. Following the discovery of reverse transciptase (RT) in retroviruses, the dogma was extended to RNA -> DNA. RT is an HIV specified enzyme essential for the replication of the virus. This enzyme is unique to HIV-like viruses and converts viral RNA into DNA, so allowing the HIV genome to be inserted into the cell’s DNA.