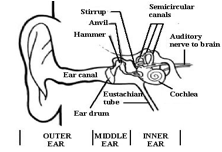
The set of neural pathways that communicates between the cochlea and the cochlear nucleus in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem. Also known as the (vestibulo)cochlear nerve, it is in fact either pair of the eighth cranial nerve that supplies the organs of hearing (via the cochlear nerve) and balance (via the vestibular nerve) in the inner ear (see figure below). Axons of the cochlear nerve synapse in the cochlear nucleus, with the ventral part synapsing on cells of the superior olives of the medulla, both on the same side and on the opposite side. The latter cells allow for the auditory localization of sounds in that they compare the timing of impulses from the left and right ears. The vestibular nerve projects to the semicircular canals that register angular acceleration via the vestibular ganglion.