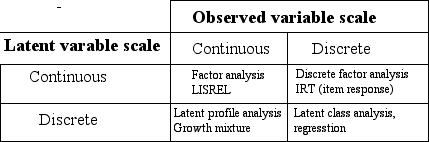
A hypothetical variable which is not directly measured but is presumed to have some influence on the scores of the observed or manifest variables. Put another way, it is a hidden commonality that has to be derived from the data generated by a group of measured variables . Statistical models that aim to explain observed variables in terms of latent variables are referred to as latent variable models such as factor analysis, latent class analysis, and latent profile analysis (e.g., the Five Factor model of personality was inferred by means of factor analysis). The choice of model depends on whether the observed variables are continuous or discrete and whether the latent variables are continuous or discrete (see table below).