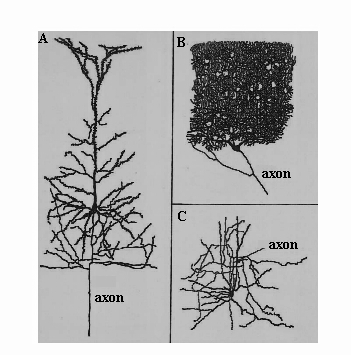
Inhibitory interneurons of the cerebellar cortex at the top of the granular layer deep to the Purkinje cells containing the neurotransmitter GABA. These cells have extensive processes that extend well into the molecular layer and the lower parts of the granular layer. They are activated by mossy fibers and climbing fibers so as to provide feedfoward inhibition to the granule cells (which shortens information coming into the cerebellar cortex via mossy fibbers), and by parallel fibbers that enable recurrent inhibition to the Golgi type II cells. Yet another discovery by Camillo Golgi (1844-1926). The figure below depicts Ramon y Cajal‘s drawings of whose original drawings of Golgi type I and II cells.