The outermost primary germ layer that originates during gastrulation (see figure below), which gives rise to the nervous system and outer integument (i.e., outer protective covering such as skin and cuticle).
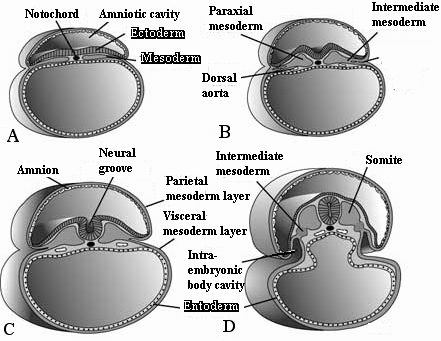
Ectoderm, along with mesoderm and entoderm, is one of three main layers formed in the gastrula during the stages of gastrulation (A-D). There are three derivatives of the ectoderm: skin ectoderm giving rise to the epidermis of the skin (as well as epidermal derivatives such as hair, glands and nails), neural crest ectoderm giving rise to a large variety of structures (e.g., adrenal medulla, autonomic ganglia, dorsal root ganglia) , and neural ectoderm giving rise to the central nervous system, including neurons and neuroglia.
See Adrenal medulla, Apical ectodermal ridge (AER), Blastopore, Blastula, Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Differentiation (embryology), Dorsal root ganglia (DRG), Embryo, Embryogenesis, Entoderm (or endoderm), Gastrula, Gastrulation, Germinal (or germ) layers, Limb bud, Mesenchyme, Mesoderm, Neural crest, Neural plate, Neurulation, Noggin, Organogenesis, Pharyngeal arches, Pituitary gland, Placode, Proliferative ventricular zone, Transforming growth factor (TGF), Vestibular system

