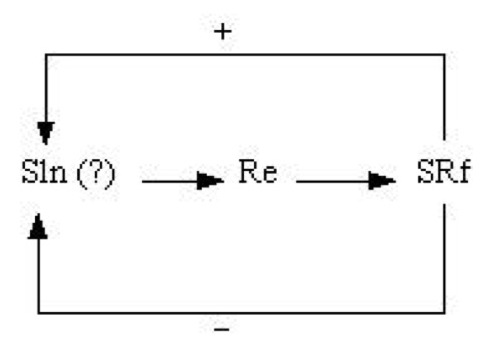
Learning the relationship between one’s own behaviour and its environmental consequences. A process of learning in which the relative frequency of a response increases as the result of a reward or reinforcement contingent on the response that is emitted (see figure below). Also called respondent conditioning and Skinnerian conditioning.
Operant conditioning: modification due to positive or negative consequences, where S1n =initial stimulus (often unknown), Re = response, SRf =reinforcing stimulus or reinforcement = consequences of behavior, + = rewardingstimulus, and – = negative or aversive stimuli (not the same aspunishment).
See Avoidance learning, Behaviorism, Classical conditioning, Delayed conditioning, Discrimination, Escape learning, Learning, Mobile conjugate reinforcement, Operant train task, Paradigm, Positive reinforcement, Reinforcement schedule, Reinforcer, Stimulus generalization