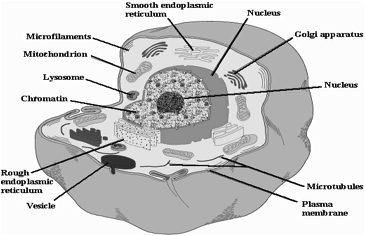
In biology, the structural and functional unit of all living organisms, which exists as an independent unit of life in bacteria and protozoans, and first described by Robert Hooke (1635-1703) in 1665 with the aid of a light microscope. In other living organisms, they form colonies or tissues. Each cell contains protoplasm differentiated into cytoplasm and a nucleus containing DNA. There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic cells as in bacteria and eukaryotic cells in which the nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and the cytoplasm is divided by membranes into connected cavities and separate compartments referred to as organelles (e.g., mitochondria and Golgi organs), as indicated in the figure below.