WP1: Concept Optimisation
This work package is focused on refining the design of the Wave Energy Converter (WEC) by improving its hydrodynamic performance and Power Take-Off (PTO) system. The goal is to optimise the WEC for maximum energy conversion efficiency by understanding and enhancing its interaction with ocean waves.
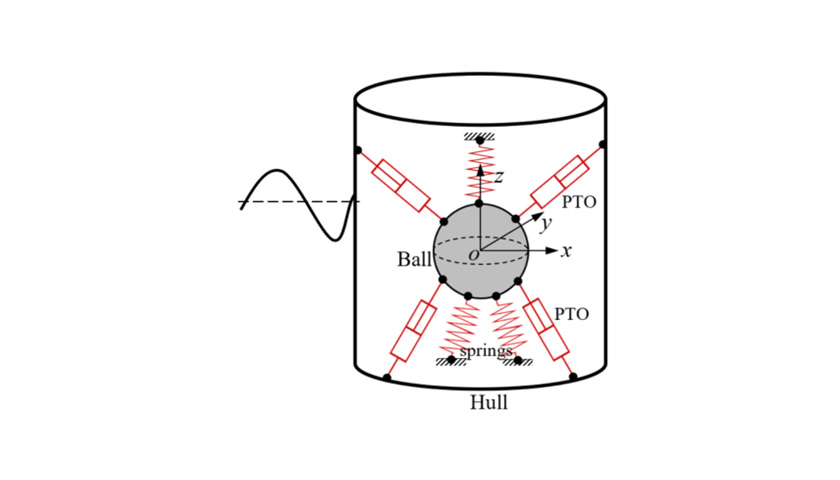
WP1.1
Experimental and Numerical Hydrodynamic Analysis
Experimental testing in wave tanks and numerical simulations are conducted to understand how the WEC behaves in different sea conditions. This step focuses on capturing the WEC's interaction with wave forces, including multi-axis wave dynamics and the influence of WEC geometry on energy capture.
WP1.1
Experimental and Numerical Hydrodynamic Analysis
Hydrodynamic behaviour is analysed under various operational conditions to assess how the device responds to regular and extreme sea states.
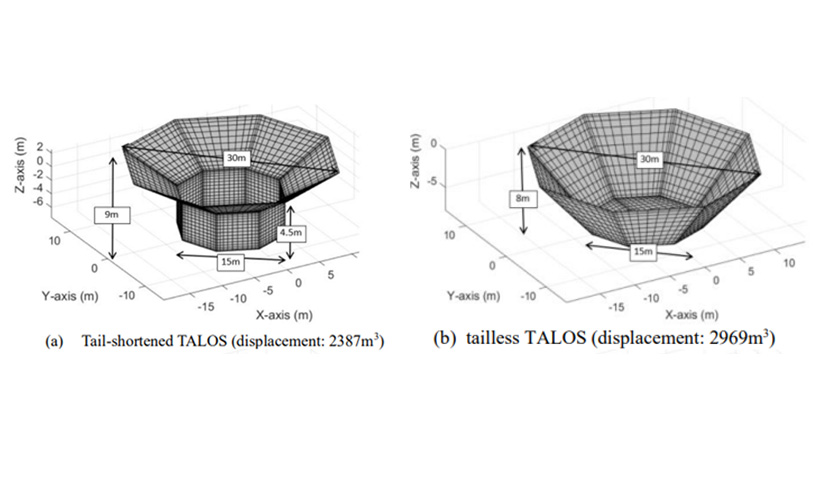
WP1.2
Geometric Optimisation
The geometry of the WEC, such as its shape and structural design, is optimized based on hydrodynamic results from WP1.1. This includes refining the device's ability to absorb wave energy from multiple directions and maximising efficiency across a range of wave conditions.
This task aims to fine-tune the external shape of the device, balancing energy absorption with durability to withstand harsh marine environments.
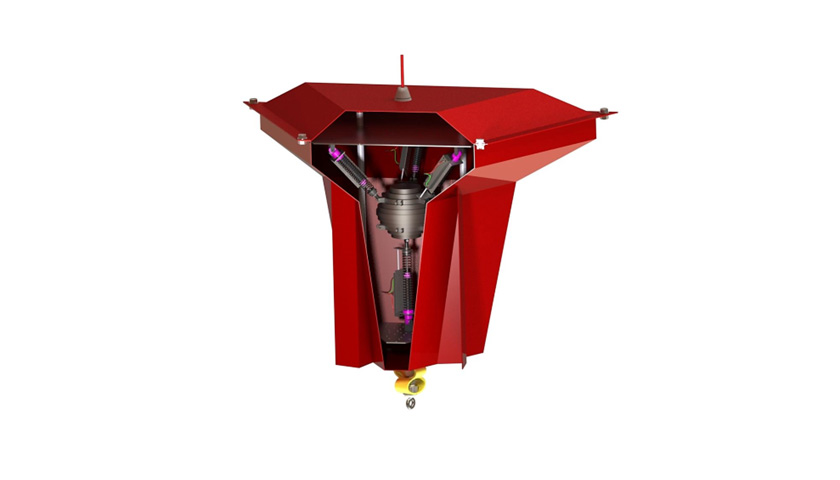
WP1.3
Power Take-Off (PTO) Design
The PTO system, which converts mechanical energy from the waves into electricity, is optimised for performance and efficiency. For the TALOS-WEC, this involves the inertial mass system, where the motion of the internal mass drives hydraulic cylinders that generate electrical power.
Specific focus is placed on the design of the hydraulic circuit and how to smooth the power output to ensure consistent energy generation.
This task also explores how the PTO system can adapt to fluctuating sea conditions.

