Visvantini Kumaran
Background: Over the years, loneliness has become a concerning issue among Malaysians especially during the Covid-19 pandemic. Previous research showed that social appearance anxiety, social media usage and relationship perfectionism are contributing factors for loneliness. Hence, this study aims to investigate relationships between these variables and social and emotional loneliness.
Methods: 136 participants were recruited using convenience sampling (Female=71%), aged between 18-35 years old and answered survey which included demographic questions, Social Appearance Anxiety Scale, Bergen’s Social Media Addiction Scale, Relationship Perfectionism Scale, and Social and Emotional Loneliness Scale.
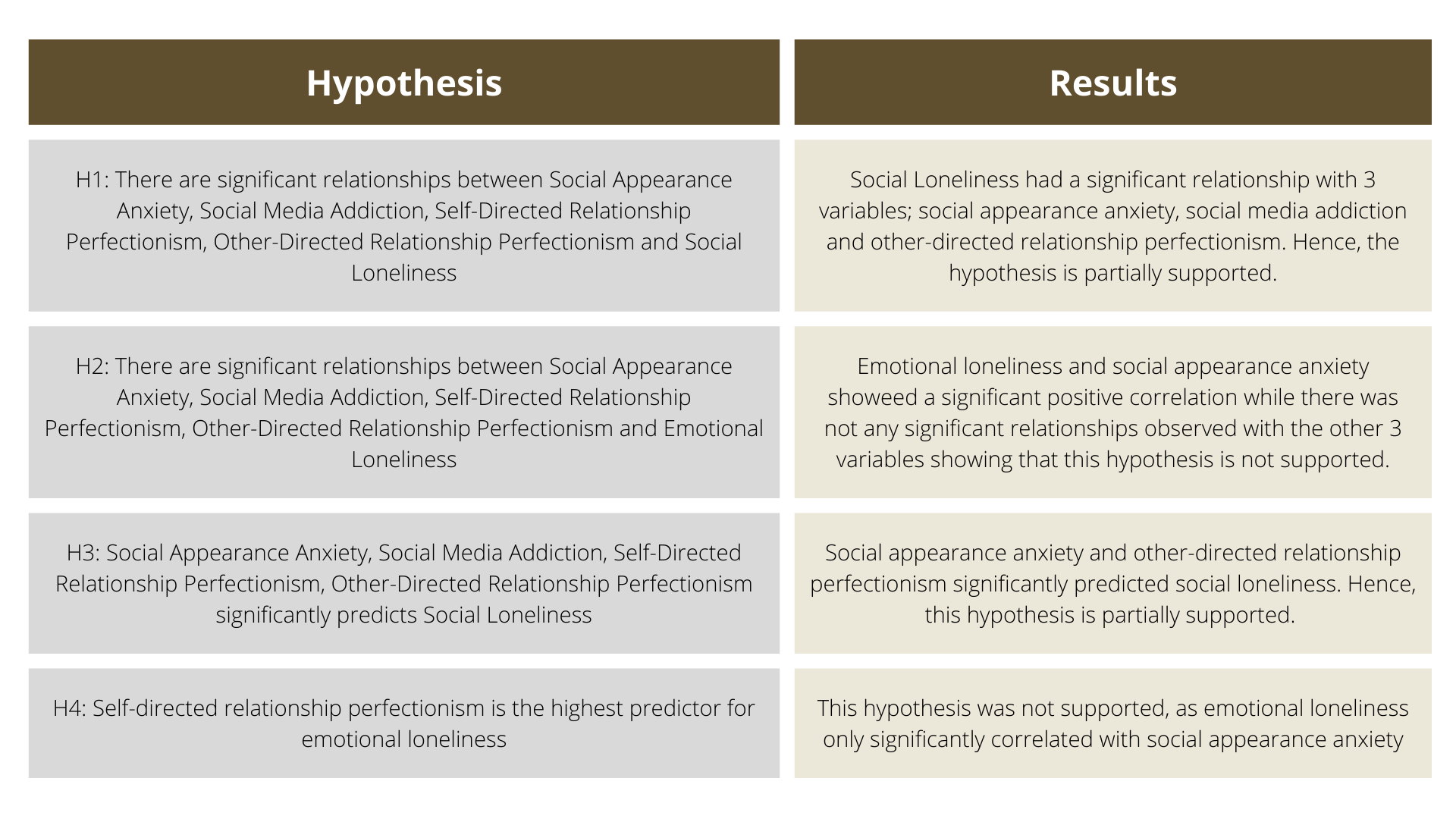
Results: Findings from this study shows that (1) social appearance anxiety, social media addiction, and other-direct relationship perfectionism have positive relationships with social loneliness; (2) social appearance anxiety have positive relationships with emotional loneliness; (3) multiple regression analysis shows that social appearance anxiety and other-direct relationship perfectionism are significant predictors of social loneliness meaning high scores in both predictors lead to high social loneliness.
Conclusion: This study shows that young adults in Malaysia may experience social loneliness due to increase in social appearance anxiety that involves self-doubt and fear of negative evaluation. Also, other-directed relationship perfectionism that involves unrealistic and excessive expectations placed on other people may result in social loneliness.

Visvantini Kumaran

Content
1. Introduction
2. Research Aim
3. Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion & Conclusion
INTRODUCTION
Loneliness: A subjective feeling of emptiness that can be caused due to distance and lack of meaningful bonds. However, an individual can experience loneliness despite being surrounded by other people.




Loneliness does not only bring harm to mental health but also physical health. Some negative effects of loneliness includes depression, suicidial ideation, heart related issues and neuroendocrine changes. Although many classifications of loneliness exist, the present study uses 2 subsections :
Social Loneliness & Emotional Loneliness
when an individual lacks quality social network such as friendships or good colleague relationships
when an individual lack intimate relationships, particularly romantic relationships. It also usually occurs when sexual relations and satisfaction in a relationship is lacking
The present study investigates on possible factors that could contribute to loneliness, which includes
1. Social Appearance Anxiety
2. Social Media Addiction
3. Relationship Perfectionism
1. Social Appearance Anxiety is the concept of negative evaluations towards physical appearance and fear of negative judgments by others. Past studies shows that social appearance anxiety begins when individuals have a mindset of self-blaming & excessive self judgment. For some, appearance is a measure of self esteem while for others, feeling unattractive decreases self-esteem. Young adults who give a low self evaluation of physical attractiveness avoid going out in public as they feel awkward when meeting others and expressing themselves. They do this to avoid self perceived evaluation of judgments of others. This process may underlie the increased likelihood of individuals with social appearance anxiety to remain isolated with pre-judgments of how society evaluates their appearance. Thus, social appearance anxiety may prohibit formation of positive interpersonal relationships among friends and family, propagating loneliness.
2. Research shows loneliness is an ongoing problem in some societies where social media usage is extremely high. The predominant motivating factors for usage of Facebook and Instagram are the need for self-representation and the need to belong. Social media users mainly focus on networking (making friends and staying in touch) and sharing media content. Sharing photos and selfies with friends are the most popular features on these platforms. The likes and comments provide the immediacy and intimacy required for simulated social presence, predisposing online communication to induce isolation of individuals offline and decrease social well-being. the instant gratification and mood boosting that these likes and comments give, are initially seen as a pleasurable experience for users to present themselves positively. As users constantly seek these short mood boosting bursts, they are incentivised to check their profiles more often and maintain a sufficient amount of engagement with their followers to maintain an attractive profile. If chronic, this behaviour can become addictive and thus require users to continuously seek validation and belonging from virtual friendships/relationships online A meta-analysis study conducted by Song et al. (2014) found that a potential cause for loneliness among active social media users were shyness and lack of social support. This is compounded by lonely individuals being prone to continuously seek social support and validation from virtual connections created online, compared to face-to-face communication
3. For a relationship to last for a long time, mutual understanding, love, and respect are essential. However, some tend to set excessively high or unrealistic expectations, which is better known as perfectionism, leading to an unhealthy relationship that causes friction between partners. Perfectionism is defined as the tendency to set inconsiderately high standards together with highly critical self-evaluations. Perfectionism results from problematic interpersonal outcomes, such as overdependence on partners/friends, neediness, and hostile behaviours. Relationship perfectionism can be classified into two forms: self-directed relationship perfectionism and other-directed relationship perfectionism. Self-directed relationship perfectionism refers to how one is involved in intrinsic, personal, and perfectionistic standards. In other words, these individuals set a high, rigid standard for themselves to achieve. Other-direct relationship perfectionism involves unrealistic and excessive expectations placed on other people by setting up rules for others to live up to one's expectations. Although a weak link has been demonstrated between self-directed perfectionism, psychopathology and suicidality, it does contribute to social disconnection, which leads to loneliness. factors underlying other-directed relationship perfectionism induce more adverse effects on one's physical and mental health, since individuals in this form are prone to be hostile and dominant.
RESEARCH AIM
The present study examines possible factors that have been associated with social and emotional loneliness among young adults in Malaysia: social appearance anxiety, social media addiction and relationship perfectionism. The present study aims to measure 3 variables as potential factors for social and emotional loneliness which are social appearance anxiety, social media addiction and relationship perfectionism.
Although there are researchers that studied what can cause loneliness, there are still a lack of studies that directly incorporates social appearance anxiety, social media addiction and relationship perfectionism and how they play a role in loneliness. The present study examines possible factors that have been associated with social and emotional loneliness among young adults in Malaysia: social appearance anxiety, social media addiction and relationship perfectionism.
METHODS

RESULTS
DISCUSSION & CONCLUSION
As the present study was conducted in 2020 during the lockdown, due to the Covid-19 pandemic, virtual communication became an alternative for many to keep in touch with friends and family. Working adults and students also relied heavily on it. Unlike face-to-face interactions, virtual communication tools provide mirroring of individual's faces on screen, allowing them to inspect their appearances constantly. This constant evaluation can increase the risk for appearance insecurity. Many individuals found themselves having body image concerns and facial dissatisfaction, due to constantly comparing their looks with others. This situation is in line with the Objectification Theory, defined as the unconscious adaptation of a third-person perspective on one's own body. Frequent self-doubt and appearance dissatisfaction prevent socializing with friends and family since they strive for social conformity, frequently leaving them feeling lonely. In addition, excessive self-focus has been demonstrated to increase social anxiety due to fear of judgment and negative impressions, which leads to avoiding social contact with others.
In contrast, this study showed that social media use did not impact social and emotional loneliness, despite having a high surge in virtual communications and internet usage during the lockdown period. This disparity could be attributed to the link between social appearance anxiety and social media usage. First, social media users, who feel high pressure about their appearance, will naturally avoid using social media as they feel uncomfortable in online situations. During the pandemic, many have turned to virtual chatting and online meetings to stay connected. During the Covid-19 pandemic, appearance dissatisfaction increased due to frequent video calling, which suggests that social appearance anxiety and social media usage act concomitantly. In addition, individuals who experience social anxiety have an increased likelihood of low self-esteem. This can impact the poor usage of social media, as they tend to avoid negative feelings and judgments from others online. Secondly, during the lockdown period, it is plausible that many users went through social media fatigue. Technology, information and communication overload regarding the pandemic occurred through increased users' participation and interactions on various platforms. According to WHO, about 60% of young adults were feeling anxious with the daily news on Covid-19. This includes information on the Covid-19 outbreak, death tolls, and economic issues associated with the lockdown. This information has been suggested to have induced fear as an adaptive response to danger, which caused many to feel overwhelmed when using social media.
This present study tested two subsections of relationship perfectionism and showed that only the other-direct relationship perfectionism lead to social loneliness, while self-directed relationship perfectionism was not a factor for social and emotional loneliness. Individuals who set high standards for themselves (self-direct relationship perfectionism) are usually motivated to achieve goals that they set for themselves. Individuals with a high level of self-direct relationship perfectionism are conscientious, ambitious, and very self-efficacious. These individuals raise the bar high for themselves to achieve their goals, and research shows that this habit induces a positive effect in facilitating them to achieve their goals. It was also demonstrated that individuals who set unrealistic expectations on themselves have a good internal locus of self-control, which is rare. This suggests that individuals with self-direct relationship perfectionism do not avoid social and emotional connections, as they set high standards for themselves to achieve. However, this mindset can be very unhealthy for many, as unrealistic expectations could lead to severe mental and physical health effects, such as depression and suicidal ideation. This study also demonstrated that other-directed relationship perfectionism was a factor for social loneliness, but not emotional loneliness. Previous research also indicated that when a person constantly places pressure on their friends or partners to behave in a way that they expect, friction can occur, which leads to an unhealthy relationship that involves low satisfaction and built-up anger. Individuals who expect too much from people around them believe that others need to be perfect around them. These individuals are also highly critical of others' actions and behaviours which causes them to draw away relationships and friendships in their life. Placing unrealistic standards towards others may cause people to drive away as they may feel overwhelmed and stressed. This could potentially account for why other-direct relationship perfectionism plays a role in social loneliness, as social loneliness is loneliness experienced from not being part of a group of friends or work colleagues. The unrealistic expectations set on themselves (self-direct relationship perfectionism) may not have affected them. Still, it is not the same scenario when these unrealistic standards are placed on other people (other-direct relationship perfectionism).
Research found that during the lockdown, family members and partners were obliged to stay close, which was comforting during the crisis. In addition, many people were more forgiving and accepting of their family or partner's negative behaviours, which lead to relationship satisfaction. Many were able to use positive coping efforts and avoid arguments or conflicts that may erode relationship satisfaction. The results of the present study could also be impacted by the participants' relationship status. 90 participants (66.75%) were not involved in romantic relationships. Studies have shown that singlehood is often assumed as miserable, low self-esteem and unhappiness. However, in reality, singlehood is viewed as an expression of individualistic attitudes and freedom of choice. Negative associations about people who are not committed in a relationship are inaccurate, as single individuals have shown to be content and happy with their lives. However, research has also shown that many single individuals would like to be in a relationship or married. Therefore, future studies focusing on romantic loneliness and singlehood are warranted, as this study measured both family relationships and romantic relationships.
Slide 1 image (max 2mb)
Slide 1 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 1 Caption
Slide 2 image (max 2mb)
Slide 2 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 2 Caption
Slide 3 image (max 2mb)
Slide 3 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 3 Caption
Slide 4 image (max 2mb)
Slide 4 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 4 Caption
Slide 5 image (max 2mb)
Slide 5 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 5 Caption
Slide 6 image (max 2mb)
Slide 6 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 6 Caption
Slide 7 image (max 2mb)
Slide 7 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 7 Caption
Slide 8 image (max 2mb)
Slide 8 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 8 Caption
Slide 9 image (max 2mb)
Slide 9 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 9 Caption
Slide 10 image (max 2mb)
Slide 20 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 10 Caption
Caption font
Text
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)