Jia Huey Gan
In what areas can higher education institutions help students improve their learning and academic achievement in online learning? The present study investigated whether motivation and self-regulation are able to predict academic achievement or perceived learning in higher education online setting. The study was conducted on 146 Malaysian undergraduates aged 18 – 25 years old (61 males and 85 females) via an online survey. Academic motivation, self-regulation, perceived learning and academic achievement were measured using a questionnaire. The main takeaway from this study is that it is better for students to have any type of motivation than no motivation at all in learning. Results showed that lack of motivation has a negative relationship with academic achievement and is a negative predictor of perceived learning. Besides, having intrinsic motivation and using self-regulated learning strategies increases one’s perceived learning. Furthermore, extrinsic motivation has a positive relationship with perceived learning but is not a significant predictor. Contrary to previous findings, intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and self-regulation did not significantly impact academic achievement. Overall, the findings imply that higher education institutions can implement changes to prevent lack of motivation and foster intrinsic motivation and self-regulation in students to encourage learning.

Jia Huey Gan
Encourage Learning in Higher Education Online Learning
The Covid-19 pandemic has greatly impacted how schools conduct their teaching. In March 2020, the Malaysian government issued a Movement Control Order to curb the spread of Covid-19 which forced higher education institutes to shift to online learning (Tang, 2020). Although online learning has benefits such as flexibility and course availability, students require discipline to complete classes and assignments without the direct guidance of lecturers or tutors (Oliveira et al., 2018). Therefore, what should students do to thrive in online learning?
The current study looked at 2 factors that could impact online learning which are motivation and self-regulation. And online learning was measured from two aspects which were academic achievement; an evaluation of learning by others, and perceived learning; a subjective learning based on the sense of new knowledge or understanding acquired (Barzilai & Blau, 2014).
This study investigated whether motivation and self-regulation would have a relationship with academic achievement and perceived learning. Furthermore, if they do, how do they predict academic achievement and perceived learning?
A photo of a young man studying using the computer with his headphones on and a pen in his hand. | Photo by Jeremy Bishop on Unsplash.
Motivation
Motivation is the psychological process that leads to arousal, direction and persistence of goal-directed voluntary actions (Mitchell, 1982)
According to Ryan and Deci (2000) we can understand motivation from the sub theory of self-determination theory, called organismic integration theory that categorizes motivation into three main motivation types:
- intrinsic motivation (doing a task for the inherent satisfaction of the task itself)
- extrinsic motivation (working to gain another outcome not directly related to the task itself)
- amotivation (lack of intention to do a task)
The theory also expands the different types of extrinsic motivation (Ryan & Deci, 2000).
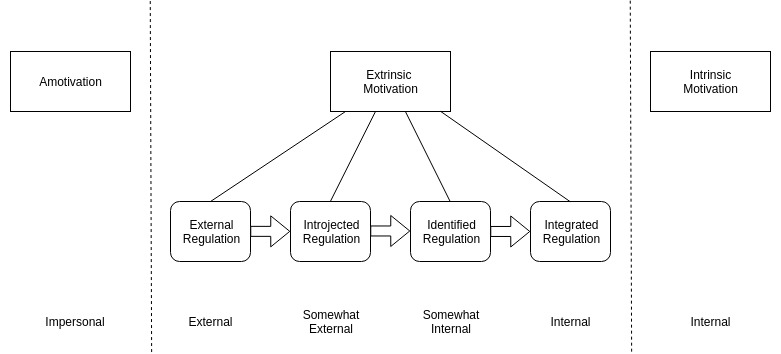
Organismic Integration Theory's continuum of motivation (Loughrey & Broin, 2018).
Self-Regulation
Based on the social cognitive theoretical perspective, self-regulation describes the use of self-regulated learning strategies, and the ability to respond to self-oriented feedback about one’s learning effectiveness and the interdependent motivation processes (Zimmerman, 1990). Self-regulation in this study measures 6 self-regulated learning strategies which are environment structuring, goal setting, time management, help-seeking, task strategies, and self-evaluation (Barnard et al., 2009).
Academic Achievement
Academic achievement is an academic outcome that is usually measured by the school which includes but is not limited to GPA, course grades, assignment marks and study points. Academic achievement in this study refers to the score of one compulsory subject.
Perceived Learning
Perceived learning refers to how much knowledge the student reports based on introspection and reflection (Bacon, 2016). Perceived learning in this study measures three domains of learning which consists of cognitive. affective and behaviour (Bloom et al., 1956).
Methodology
This study used an online survey as the data collection method. 146 responses from participants who were full-time Malaysian undergraduate students who have recently completed and gotten back their results for an academic semester of a minimum of 14 weeks and had undergone a minimum of 60% online learning were included in the study.
The questionnaire collected data about 5 things:
- Demographic information (gender, age, nationality, Malaysian tertiary students status and diagnosis of learning disability)
- Information about the core subject in their programme (completion of long academic semester, number of subjects taken, percentage of online teaching mode for that subject)
- Academic Motivation Scale (Vallerand et al., 1992)
- Online Self-Regulated Learning Questionnaire (Barnard et al., 2009)
- Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor Perceived Learning Scale (Rovai et al., 2009)
Results
A Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient was used to test whether there was a relationship between the independent variables (intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, amotivation and self-regulation) and the dependent variables (academic achievement and perceived learning).
If there was a relationship found, a linear regression or multiple regression would be conducted to find out whether the independent variable could predict the dependent variable and in what direction.
The table below summarises the findings from these tests.
Intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and self-regulation were not associated with academic achievement. This means that there was no relationship found between these independent variables and academic achievement. However, amotivation was found to be a significant negative predictor of academic achievement. This would suggest that the higher the amotivation, the lower academic achievement.
Next, intrinsic motivation and self-regulation were significant positive predictors of perceived learning. This means that if a person's intrinsic motivation or self-regulation increases, the perceived learning would increase as well. Conversely, amotivation was a significant negative predictor of perceived learning. Therefore, if amotivation increases, perceived learning decreases. Lastly, extrinsic motivation had a significant positive correlation with perceived learning. This suggests that extrinsic motivation has a positive relationship with perceived learning but it could not predict perceived learning.
Discussion / Implications
What do these results mean to you?
Looking at our results in light of the findings of past research, this study suggests that students, lecturers, school counsellors and higher education institutions could pay attention to a few things...
Amotivation
- Amotivation plays a significant role in perceived learning and academic achievement in higher education online learning as it could lead to dropouts.
- School counsellors could prevent dropouts by identifying students who are amotivated (using absenteeism indicators and collaborating with lecturers) and providing necessary interventions based on the students’ needs (such as group counselling) (Blount, 2012).
Intrinsic Motivation
-
Intrinsic motivation is important in perceived learning for students in higher education online learning.
-
Higher education institutions could redesign their course to foster intrinsic motivation in students throughout their years in university based on the three psychological needs; competence, autonomy and relatedness (Ryan & Deci, 2000).
Self-Regulation
- Self-regulation is crucial in perceived learning of students in higher education online learning.
- Higher education institutions could promote self-regulation in students for online learning by teaching self-regulation (Wandler & Imbriale, 2017) and developing a learning environment that encourages self-regulation (Mcmahon & Oliver, 2001).
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my appreciation to my supervisor Ms Elaine Yong for her guidance, advice, support and patience throughout the planning, execution and writing of this dissertation. Next, I would like to thank my college lecturers Mr Kamarul and Ms Thasha for allowing me to promote my survey to their students. Lastly, I'm thankful to God, my family and friends for their support.
References
Bacon, D. R. (2016). Reporting actual and perceived student learning in education research. Journal of Marketing Education, 38(1), 3-6. https://doi.org/10.1177/0273475316636732
Barnard, L., Lan, W. Y., To, Y. M., Paton, V. O., & Lai, S. L. (2009). Measuring self-regulation in online and blended learning environments. The Internet and Higher Education, 12(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2008.10.005
Barzilai, S., & Blau, I. (2014). Scaffolding game-based learning: Impact on learning achievements, perceived learning, and game experiences. Computers & Education, 70(1), 65-79. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.08.003
Bloom, B. S., Engelhart, M. D., Furst, E. J., Hill, W. H., Krathwohl, D. R. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives. David McKay Company.
Blount, T. (2012). Dropout prevention: Recommendations for school counselors. Journal of School Counseling, 10(16), n16.
Loughrey, K., & Broin, D. O. (2018). Are we having fun yet? Misapplying motivation to gamification. IEEE Games, Entertainment, Media Conference 2018, http://doi.org/10.1109/GEM.2018.8516535
McMahon, M., & Oliver, R. (2001). Promoting self-regulated learning in an on-line environment. Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE) 1299-1305.
Mitchell, T. R. (1982). Motivation: New directions for theory, research, and practice. Academy of Management Review, 7(1), 80-88. https://doi.org/10.2307/257251
Oliveira, M. M. S., Penedo, A. S. T., Pereira, V. S. (2018). Distance education: advantages and disadvantages of the point of view of education and society. Dialogia. 29(1), 139-152. https://doi.org/10.5585/dialogia.N29.7661
Rovai, A. P., Wighting, M. J., Baker, J. D., & Grooms, L. D. (2009). Development of an instrument to measure perceived cognitive, affective, and psychomotor learning in traditional and virtual classroom higher education settings. The Internet and Higher Education, 12(1), 7-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2008.10.002
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.1037110003-066X.55.1.68
Tang, K. H. D. (2020). Movement control as an effective measure against Covid-19 spread in Malaysia: an overview. Journal of Public Health, 1-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01316-w
Vallerand, R. J., Pelletier, L. G., Blais, M. R., Briere, N. M., Senecal, C., & Vallieres, E. F. (1992). The academic motivation scale: A measure of intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivation in education. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 52(4), 1003–1017. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0013164492052004025
Wandler, J. B., & Imbriale, W. J. (2017). Promoting undergraduate student self-regulation in online learning environments. Online Learning, 21(2), n2.
Zimmerman, B. J. (1990). Self-regulated learning and academic achievement: an overview. Educational Psychologist, 25(1), 3–17. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep2501_2
Slide 1 image (max 2mb)
Slide 1 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 1 Caption
Slide 2 image (max 2mb)
Slide 2 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 2 Caption
Slide 3 image (max 2mb)
Slide 3 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 3 Caption
Slide 4 image (max 2mb)
Slide 4 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 4 Caption
Slide 5 image (max 2mb)
Slide 5 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 5 Caption
Slide 6 image (max 2mb)
Slide 6 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 6 Caption
Slide 7 image (max 2mb)
Slide 7 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 7 Caption
Slide 8 image (max 2mb)
Slide 8 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 8 Caption
Slide 9 image (max 2mb)
Slide 9 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 9 Caption
Slide 10 image (max 2mb)
Slide 20 video (YouTube/Vimeo embed code)
Image 10 Caption
Caption font
Text
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Image description/alt-tag
Image caption
Image link
Rollover Image (max size: 2mb)
Or drag a symbol into the upload area
















Border colour
Rotate
Skew (x-axis)
Skew (y-axis)
