
Lancine Conde
This research aims at identifying the potential uses of chatbots in the educational context for improving current e-learning platforms which suffer from poor course completion and user retention rates. Chatbots are conversational robots that make use of natural language processing and machine learning to converse with users over a chatroom. They are already being deployed in a variety of fields but are still mostly used in marketing.
This research will ultimately see the construction of a chatbot tutor prototype for teaching basic to intermediate French to English speakers. It will try to bring in the more personal and dynamic dimension that traditional e-learning platforms lack by mirroring the relationship between a tutor and a tutee. The bot will also be made to be as autonomous as possible.
Chatbot building tools have tremendously improved during the past five years and now require few to no programing knowledge to use, meaning that anyone can get a bot running in a matter of days. Therefore, it may be the right time for educators to start looking into chatbots as a novel way to dispense their knowledge.

Lancine Conde
Points of failure analysis
Following a literature review, the most common concerns identified for e-learning were:- The sense of isolation and feeling of loss for the learners
- The overall lack of communication with tutors and other students
- The fact that tutors cannot attend to everyone
- Ineffective & unadapted course designs because tutors are not adapting the content to the platform
- Some inadequate and confusing learning platforms
- Tutors and learners being out of touch with the technology
Possible solution
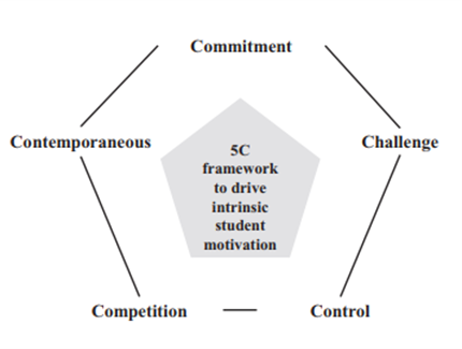
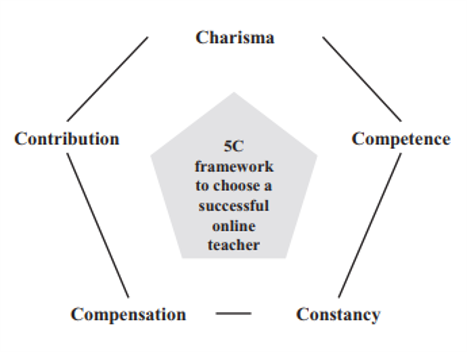
What are conversational agents?
OK, but why chatbots for e-learning?
- They can be used to provide an interactive learning experience to increase engagement
- They can also mirror the relationship between a tutor and tutee
- Learners tend feel less complexed than when facing a human and are more likely to ask the bot questions
- The bots can also be ran 24/7 over many channels making them perfectly scalable
- Most people are already used to chatting over chatrooms so they'll feel right at home
Sure, but how would it teach?
Intents, entities, context, rich replies… All of this sounds complicated...
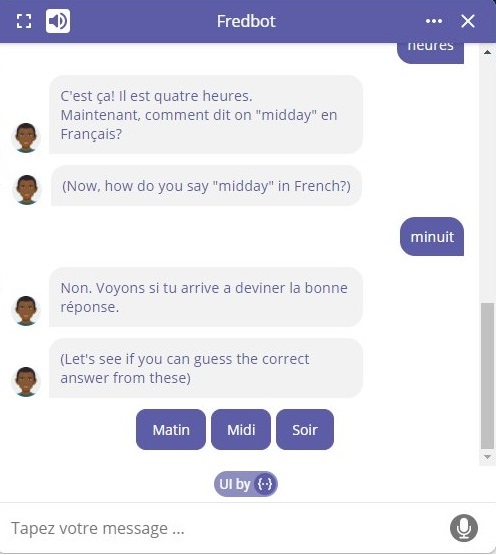
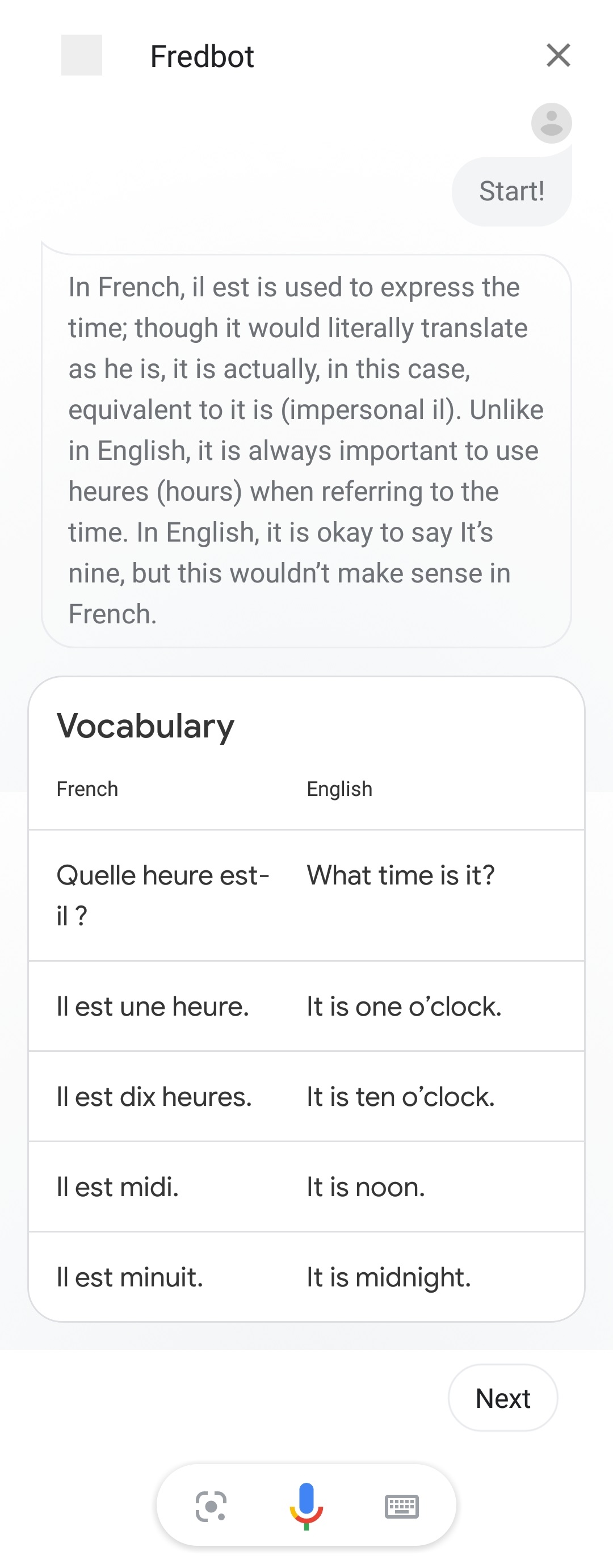
Can I see a few examples?
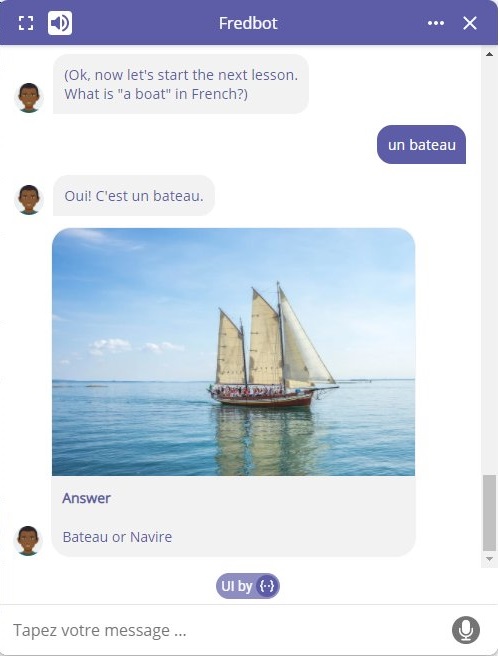
Alright, thank you Fredbot. That was very informative.
Hello, my name is Fredbot and today I will walk you through this presentation on e-learning and chatbots
Research aim
- Despite a 29% growth in student enrollment in 2020 it is predicted that there will be a 6,1% decline in market value for self-paced learning until 2021 (Tamm 2020)
- An edX study estimated that only 3,13% of registrants completed their courses in 2017-18 (Lederman 2019)
How can current e-learning platforms be upgraded to improve learner engagement and retention?
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my appreciation to my assigned supervisor Dr. Frederick Kofi de Heer-Menlah for his valuable and constructive suggestions during the planning and development of this research work. I would also like to thank Dr. Govindha Yeluripati and all the teaching staff at Lancaster University Ghana.References
- Pappas, C. (2019) Top 20 eLearning Statistics For 2019 - eLearning Industry (2019). Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/top-elearning-statistics-2019 .
- Tamm, S (2020) 100 Essential E-Learning Statistics for 2020 | E-Student (2020). Available at: https://e-student.org/e-learning-statistics/ .
- Lederman, D (2019) Study offers data to show MOOCs didn't achieve their goals | Inside Higher Ed (2020). Available at: https://www.insidehighered.com/digital-learning/article/2019/01/16/study-offers-data-show-moocs-didnt-achieve-their-goals.
- Bawa, P. (2016). Retention in Online Courses: Exploring Issues and Solutions—A Literature Review Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244015621777
- Chakor, YA. El Faddouli, NE. (2016). Abandonment of Learners MOOC Problematic Analysis and Proposed Solutions. Available at: https://www.ijcaonline.org/archives/volume153/number2/chakor-2016-ijca-911977.pdf
- Kaplan, A. Haenlein, M (2016). Higher education and the digital revolution: About MOOCs, SPOCs, social media, and the Cookie Monster. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303357021_Higher_education_and_the_digital_revolution_About_MOOCs_SPOCs_social_media_and_the_Cookie_Monster
- Olney, A. M. (2018). Using novices to scale up intelligent tutoring systems. Available at: https://olney.ai/category/2018/11/27/braintrust-iitsec.html
- Tamayo, P. Herrero, A. Martín, J. (2020) Design of a chatbot as a distance learning assistant Available at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1260231.pdf .
- Adamopoulou, E. and Moussiades, L. (2020) "An Overview of Chatbot Technology", IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, pp. 373-383. https://doi:10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_31
- Suta, P. Lan, X. Wu, B. Mongkolnam, P. Chan, J. (2020) An Overview of Machine Learning in Chatbots Available at: http://www.ijmerr.com/uploadfile/2020/0312/20200312023706525.pdf .
- Blackburn, G. (2019). How Chatbots Could Be The Future Of Learning. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/chatbots-future-learning .
- Wilson, A. (2020) 5 Ways Chatbots Can Help Students in Distant Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic - The Chatbot, The Chatbot. Available at: https://thechatbot.net/chatbots-students-covid-19/
- Colace, F et al. (2018) Chatbot for E-Learning: A Case of Study. Available at: http://www.ijmerr.com/uploadfile/2018/0831/20180831043721869.pdf .
- https://dialogflow.cloud.google.com
- https://www.botcopy.com
- Avatar made using https://avatarmaker.com

Fredbot has exited the conversation